20 News Text Classification
This is the final project of EE 660, USC.
To see more about the project, please click here.
Abstract
In this problem, I will use 20 news text data set with supervise learning and transfer learning. I will first use word embedding method to preprocess the data. In supervise learning part, I will try different classification model to classify the data and make comparison. Pick up the best model and test it on the test set. In transfer learning part, I will separate the data again to fit for the transfer learning problem. Then try Subspace Alignment, Tr Ada Boost, and Importance Weighting combine with the supervise learning model. Finally, I will analyze the result and make conclusions.
This is a classification problem. The dataset combined with 20 classes of news, which include computer topic, recreation topic, science topic and so forth. And my goal is to classify 20 news datasets. My work includes 2 parts, machine learning part and transfer learning part.
Then in part 2, I will try different transfer learning methods combine with the stage 1 models. Not all the methods are fitful for this problem, thus I will compare the results and pick the most fitful one. This transfer learning part is also useful in some cases. For example, we have lots of machine learning news with a few of deep neuron network news since it is a new topic these years. The information gained from machine learning news can help us build a better model for the deep neuron network news by transfer learning strategy.
click here to view the report.
1. classification
1.1 Data Set
The dataset I use is 20news dataset, which has several top-level categories, and for each top-level category it has many second-level categories, and even third-level categories.
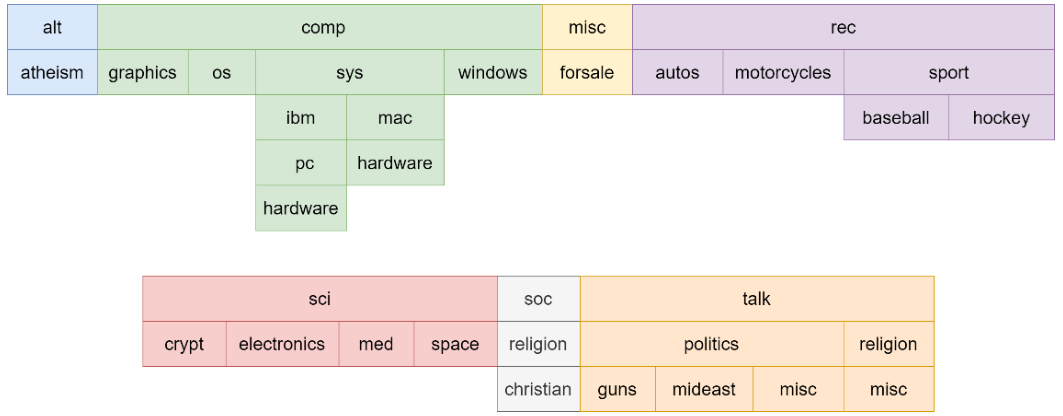
From the plot above, there are 7 top-level categories, and 20 sub-level categories. For each category, it has the numbers of data as the following table show.
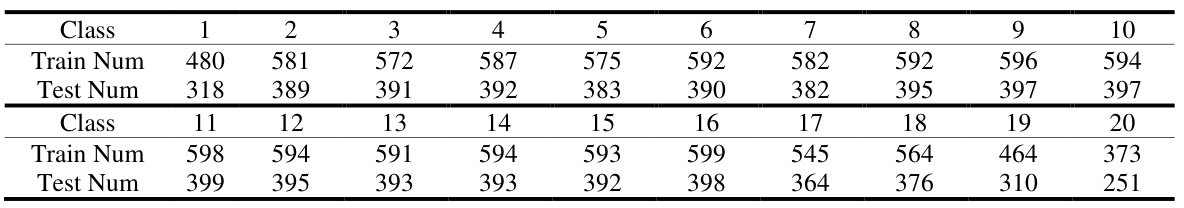
There are totally 11269 train data points, and 7505 test data points. The maximum variation of the dataset is 1.61. So, the dataset is balanced when only considering the sub level category.
1.2 Technical roadmap
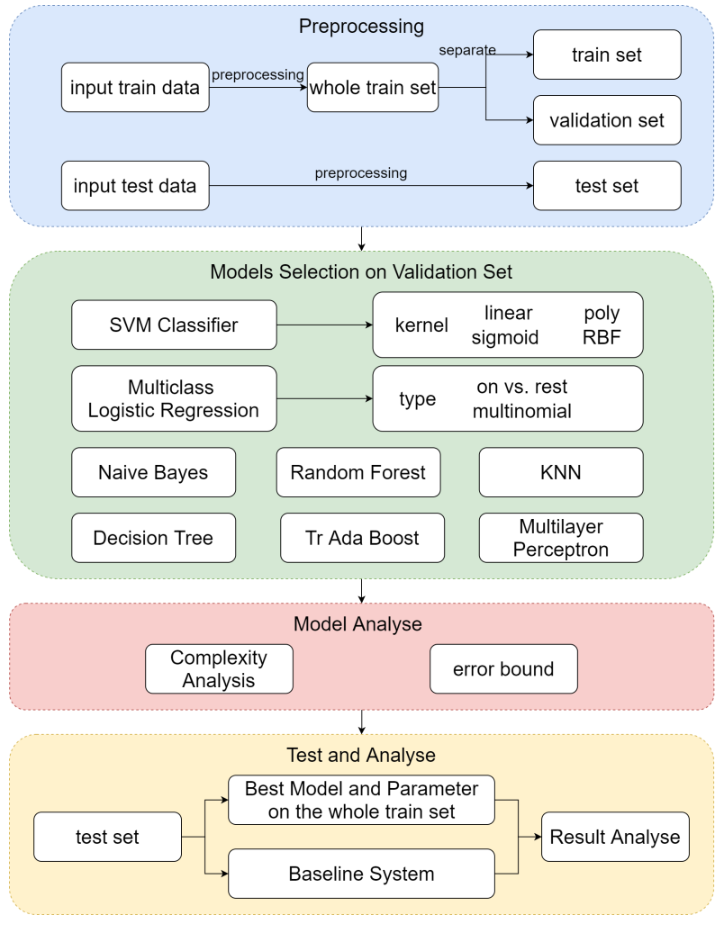
1.3 Model Selection and Comparison of Results
Result for train set (not the whole train set). All the model that accuracy higher than 0.99 is bold.

Result for validation set. All the model that accuracy higher than 0.8 is bold.

I pick up all the models that accuracy greater than 0.8 on the validation set, and calculate the accuracy on each class, and here is what I got. From the figure below, we can find that all of the model are not good at classify comp.os.ms-windows.misc, comp.sys.ibm.pc.hardware, comp.windows.x, and sci.electronics.
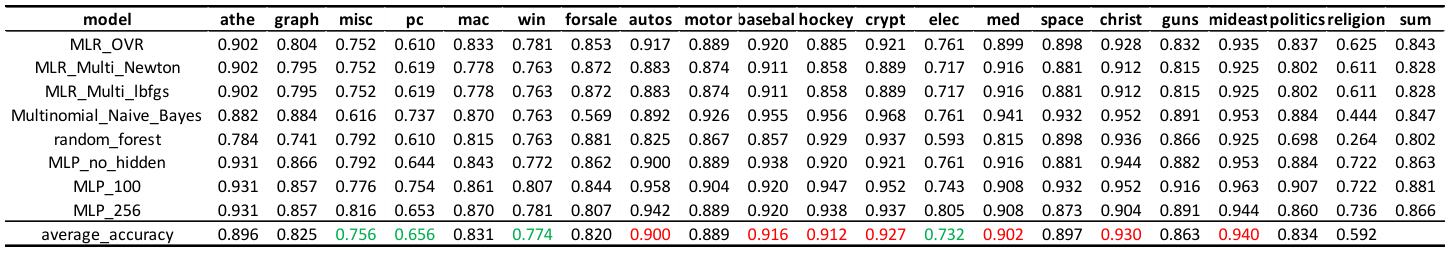
Final Results and Interpretation:
I will only use two baseline models (trivial one and SVM with linear kernel) to make the comparison with the best model, which is Multilayer Perceptron with 100 nodes in the hidden layers. Use adam for gradient descent strategy, learning rate = 0.0001, batch size = 200, epoch = 100, use ReLU as activation function. This time, I train these 3 models on the whole training set, and test it on the test set.
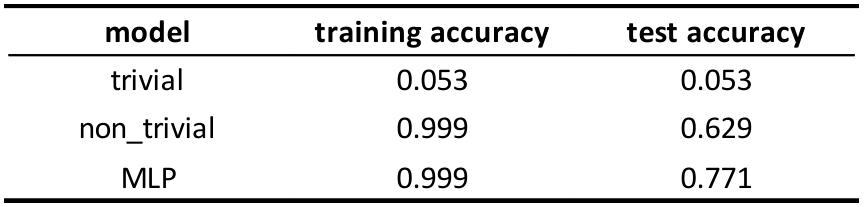
From the result, we can find that the accuracy of both the MLP and not trivial models decrease from the validation set, I guess maybe the training set is slightly different from the test set. The out-sample error bound is:
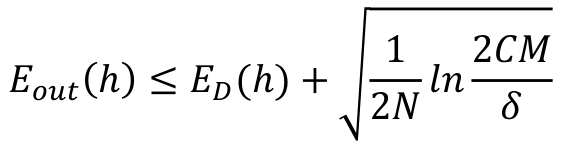
In this case, C = 20, let’s suppose δ = 0.1.
In the validation step, N = 9016, M = 24. So, the bound is 0.023
In the test step, N = 11269, M = 1. So, the bound is 0.016
2. Transfer Learning
2.1 Data Set
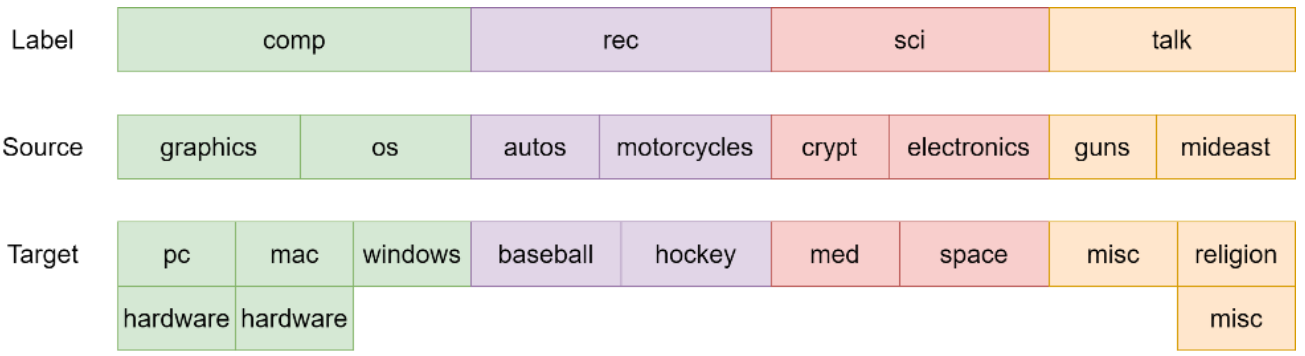
I will use “comp”, “rec”, “sci”, “talk” as 4 top layer label, and label the corresponding data points as 0, 1, 2, and 3. For each top layer group, I will select the first two subgroup as source domain data, and the remaining as the target domain data.
2.2 Technical roadmap
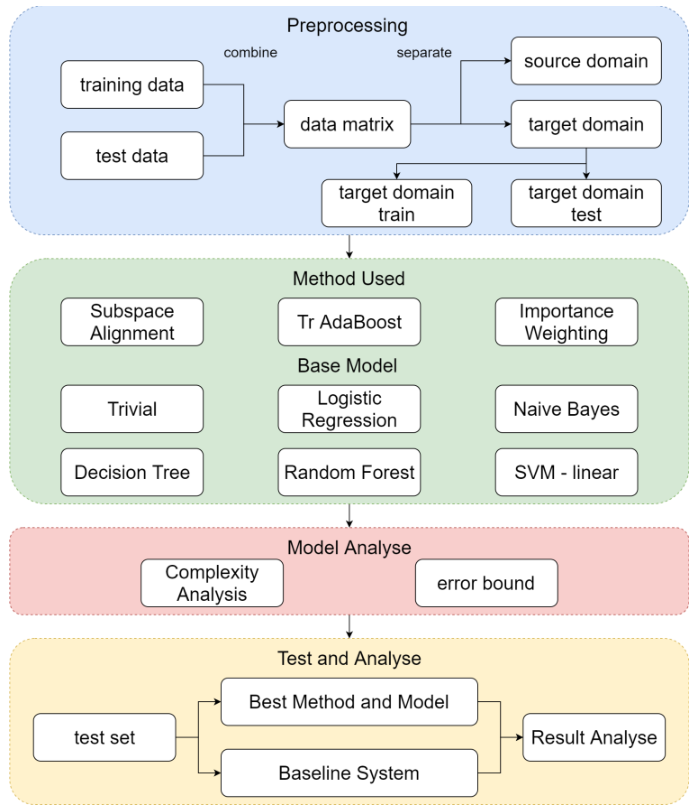
2.3 Model Selection and Comparison of Results
SA method cannot use Naïve Bayes, because Naïve Bayes request all the input data should be positive, however, when doing the transformation, some of the data will become negative. Therefore, there are no Naïve Bayes result in SA

From the result, I conclude that:
The classification accuracy for different group is vary model by model. When use baseline transfer learning (without using transfer learning) with SVM linear kernel, the highest accuracy is “talk” group. However, in Naïve Bayes, the highest accuracy group is “computer”. Therefore, we can’t say which group’s source domain and target domain is closer to each other.
SA method is always worse than baseline. Because SA is good at handling low dimension data, and it need some labeled target domain data to help it “flip” the prediction. In this problem, the data is high dimensional, it is not suitable for this method. Adjust the data distribution in the source domain will make the model predict the wrong result.
From the table above, Tr Ada Boost is always better than baseline. Because Tr Ada Boost is the only model here using target domain data and label to help it adjust the weight value. It is target oriented, always use target data and label to make the model perform better on the target domain.
Only consider the error bound on the best performance model, which is using Tr Ada Boost and Naïve Bayes.
The out-sample error bound is:
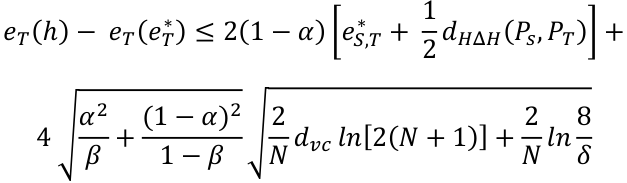
Where α: importance of error in target domain, suppose it is 0.5
β: fraction of labeled data points drawn from target domain, in this case is 7735/ (7735+4140) = 0.651
eS,T* : is the combined error = minh∈H {eS(h) + eT(h)}. I retrain and make prediction on the source and target domain again, and get 0.255.
dHΔH(PS, PT): Symmetric difference hypothesis divergence = 2, suppose it is 0.1 in this case.
In this case, N = 16015, dvc = 2 (total 4 classes), let’s suppose δ = 0.1.
The final error bound is: 0.54.
3. Summary and conclusions
Text data is completely different with all other data I have handled before. It is sparse and high dimensional, which require some new strategy to deal with. Over all the models I use, whatever in the supervise learning part or the transfer learning part, SVM with linear kernel, Naïve Bayes, Random Forest, and Logistic Regression is always good choices for handling text data.
In this project, I only use one-hot encoding method to preprocess the text data, in the future, I may try other word embedding method in NLP and see whether it perform better or not.